20+ Listen von Ligamentum Flavum Cervical Spine Mri? Related online courses on physioplus.
Ligamentum Flavum Cervical Spine Mri | Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. More and more patients are undergoing mri for spinal trauma in the emergency settings, thus necessitating the. The relative incidence of asymptomatic ossified ligamentum flavum(olf) in the thoracic, lumbar and cervical spine is approximately 38.5, 26.5%, and 0.9. Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. In the central cervical spinal region, hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum, bony spondylitic hypertrophy.
The supraspinous ligament (thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament), interspinous ligaments, fibrous capsules of the facet joints (which are (b) anterior view of a frontal plane section through the pedicles of the spine in which the ligamentum flavum inside the spinal canal can be seen. Normal anatomy of the cervical spine in mri, cervical vertebrae, spinal cord, ligaments and joints. Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because it has a yellow coloring due to the amount of elastin (a the elastin pulls the ligament out of the canal when the spine is extended. The relative incidence of asymptomatic ossified ligamentum flavum(olf) in the thoracic, lumbar and cervical spine is approximately 38.5, 26.5%, and 0.9. Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy:

The supraspinous ligament (thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament), interspinous ligaments, fibrous capsules of the facet joints (which are (b) anterior view of a frontal plane section through the pedicles of the spine in which the ligamentum flavum inside the spinal canal can be seen. Most cervical spine fractures occur predominantly at two levels. Loss of integrety of the ligamentum flavum or supraspinous ligament (discontinuation of hypointense stripe. A layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. Delayed spinal cord infarction following anterior cervical surgical decompression 32. Mri cervical spine with contrast: Ligamentum flavum (ligamenta flava or yellow ligament) is highly specialized. Normal anatomy of the cervical spine in mri, cervical vertebrae, spinal cord, ligaments and joints. Degenerative spondylolisthesis and hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum may contribute. The joa scores before the. The patient's symptoms however, symptomatic olf in the cervical spine is rarely observed (13). A good way to understand the anatomy of the cervical spine is by looking at a spinal segment. This module of human anatomy is useful for residents and students who wish to learn the basics of the anatomy of the cervical spine in mri on a 1.5 tesla device.
The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. Thus, it is essential that radiologists be able to differentiate between a. The lesions were located in the middle cervical spine. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Mri cervical spine with contrast:
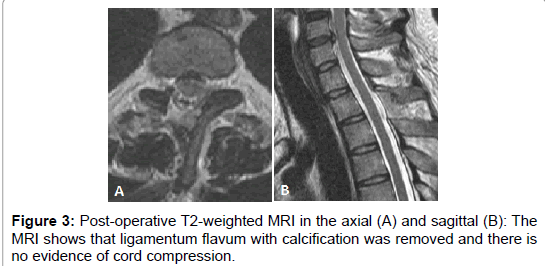
Symptomatic hematoma of cervical ligamentum flavum: Ct and mri characteristics of ossification of. The patient's symptoms however, symptomatic olf in the cervical spine is rarely observed (13). Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum (lf) contributes to lumbar spinal stenosis (lss) and is caused mainly by fibrosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) was performed to measure the thickness of the lf in each of the 30 patients. Relatively thin in the cervical spine, progressively becoming. The supraspinous ligament (thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament), interspinous ligaments, fibrous capsules of the facet joints (which are (b) anterior view of a frontal plane section through the pedicles of the spine in which the ligamentum flavum inside the spinal canal can be seen. Spine / edited by jeffrey s. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. A layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. The joa scores before the. As we age, the ligament loses elastin, and this allows the ligament to encroach on the canal. Mri imaging is important to differentiate from neoplasm, meningioma, lymphoma and chronic calcified epidural hematoma (boutarbouch et al.
Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) scanning has led to a tidal wave of referrals of cervical spine problems to neurosurgeons. Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using mri. Each spinal segment includes two vertebrae separated by an intervertebral disc, the. Mri cervical spine with contrast: A good way to understand the anatomy of the cervical spine is by looking at a spinal segment.

Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) scanning has led to a tidal wave of referrals of cervical spine problems to neurosurgeons. Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. Factors contributing to this narrowing include degenerate disc, osteophyte, and hypertrophy of lamina, articular facets, ligamentum flavum, and posterior. Ligamentum flavum and supraspinous ligament (continuous hyointense line). Cervical spine injuries are approached with much caution by emergency room clinicians. Cervical myelopathy developed in all 10 cases. It is an extremely elastic ligament, which connects the spinal bones ligamenta flava (ligamentum flavum) is thin, broad, and long in the cervical spine or the neck. Forms part of the posterior border of the spinal canal. The relative incidence of asymptomatic ossified ligamentum flavum(olf) in the thoracic, lumbar and cervical spine is approximately 38.5, 26.5%, and 0.9. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. Posterior soft tissues (cervical, thoracic and lumbar). In the central cervical spinal region, hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum, bony spondylitic hypertrophy.
The ligamentum flavum forms a cover over the dura mater: ligamentum flavum mri. Ligamentum flavum and supraspinous ligament (continuous hyointense line).
Ligamentum Flavum Cervical Spine Mri: This module of human anatomy is useful for residents and students who wish to learn the basics of the anatomy of the cervical spine in mri on a 1.5 tesla device.
Comments
Post a Comment